Getting help
Powershell is an excellent tool in that, all the required documentation is built into the shell itself. You do not have reference and developer documentation etc., as you do a lot with vbscript.
help <cmdlet or alias>
will give you the needed help required with the syntax. If you need a more detailed help explaining all the options or examples, then just use the switch –detailed or –full
help <cmdlet or alias> –full
help <cmdlet or alias> –detailed
eg: help <Get-ChildItem> –full
Help feature also supports wildcards. ie., if you are looking for a cmdlet to stop a process, then you could simply “help *process* ” as shown below:
from the above, it is relatively easy to figure out that, “Stop-Process” is the cmdlet, you can use to stop a process. Quite powerful isn’t it.
Working with Aliases
Using Aliases instead of cmdlets is convenient. ‘causing typing long cmdlet names is not only cumbersome, its also prone to mistakes, and you easily get frustrated if you use them regularly. So, to keep your sanity, PowerShell provides the alias feature. If you are from the *nix world, then you already know what alias is. Aliases can be used to call the cmdlets with shorter names for convenience instead of using their full cmdlet names.
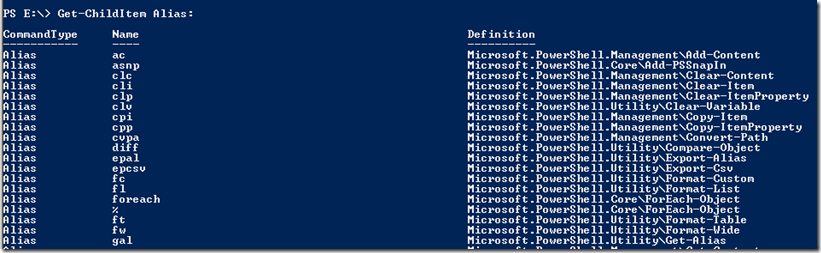
dir, ls, copy, cd are system assigned aliases for Get-ChildItem, Copy-Item, and Set-Location. PS has many more aliases and to list them, you can use the command…..wait, how can we find out what command do we use…let’s try using help here.
Looking at the output, I am tempted to try “Get-Alias”
That’s it. That how we explore the power of PS.
If I want to know the available aliases for Get-ChildItem, then I have to look at help to see all the option and switches provided by the cmdlet.
PS> help Get-Alias –full
shows this interesting example
Exactly what we need. Now let’s try that.
Understanding the above command in its simplest form(don’t get hung up on the functions, neither will I), its piping the output of the get-alias command and filtering out only the data where “Get-ChildItem” exists in Column “Definition”. Awesome…. Now this means, that PS also supports piping.
You can create your own aliases using the “New-Alias” command option. We have seen this in the second screenshot (help *alias*). The command syntax can be obtained by looking up help on New-Alias.
In its simplest form, you can use the command as below:
PS> New-Alias –name d –value GetChildItem
or
You could also specify it as below:
PS> New-Alias d GetChildItem
‘cause PS does not require you to specify the positional parameter name, if its specified in the right order. ie., in this case the first parameter that New-Alias takes is “-name” and the second parameter that it takes is “-value”. As long as we have the right values in the right order, PS will interpret them properly.
To check if the command worked, lets retry the get-alias command using where_object filtering:
Yes, “d” does show up as an alias. Lets run the command:
Delete an Alias
I’m not sure if you remember the screenshot from Day One, which reveals that Alias is also loaded as a PSDrive. which means I can also get a list of aliases by issuing a “Get-ChildItem” or “dir” against it as shown below:
which also will probably allow me to use “Remove-Item” to remove any alias that I do not need. Let’s try it.
Yup. That worked.
Finding the required cmdlet
In the beginning of this post, we used “help” command to search for required cmdlets. This is only looking at the documented help topics to get you the required information. If there are cmdlets that are not documented, then you would not find them. To find any cmdlet, you should ideally use the “Get-Command”.
Just issuing “Get-Command” by itself will list all the available cmdlets in the shell.
To understand the syntax of Get-Command let’s run “help Get-Command”
Notice the “-verb” and “-noun” parameters. This is what makes Get-Command powerful and useful in searching cmdlets. Remember on Day One we talked about how PS uses verb-singularnoun convention to name all its cmdlets. The power of doing so is revealed now.
eg: you want to look for a process on your machine and kill it, and we obviously do not know the cmdlet to do that. So lets use Get-Command to achieve this. Since we want to look at process let’s ask for all command lets that match the noun process.
So, we have two choices with processes. “Get-Process” and “Stop-Process”. See how powerful and easy it makes finding cmdlets. In addition to this the parameters support wildcards too as shown below
PS Snap-ins
Cmdlets themselves are packaged in snap-ins. Each snap-in adds additional functionality and cmdlets to the shell. Very much like mmc snap-ins. The cmdlets used to manage snap-ins can be found by using the Get-Command described above.
We can make an educated guess, that Add-PSSnapin is to add new Snap-ins and Remove-PSSnapin is to remove Snap-ins from the shell. Get-PSSnapin is probably used to get details about a Snap-in. Let’s check.
As evident, running Get-PSSnapin, when run by itself, lists all the available snap-ins on this computer. We also notice that it can used to search for a particular snap-in using the –name parameter, which also accepts wildcards. In this case, we tried to look for any snap-in that has the word “Utility” in it.
To see available cmdlets in a snap-in, we may have to look at Get-Command cmdlet’s syntax more closely.
oh, wait, yes, Get-Command takes –pSSnapIn as an argument. Wonderful. Let’s try that: