Running Windows XP as the non-admin is one of the primary safeguards you can take to protect yourself. Remove your active user account from administrator group and the Power User group, or create a normal user account and start using that account instead. Always make the regular user account member of Network Operators group. This will enable them to change their network setting like IP address and gateway etc.,
It is relatively easy to upgrade your privileges to an admin account in order to install software or run any other administrative tasks if required. The simplest form of this is to run a command prompt as administrator and run all your administrative tasks from that command window.
c:\> runas /user:administrator cmd.exe
This will open up a command prompt and ask you for the password of the local user account “administrator”. Provide that and if successful, it will launch a plain old command prompt console. From here you can launch or perform most of the administrative tasks including install new softwares, IE plugin’s etc., The command to launch most common applications are listed below:
Task
TASK
Command
Add/Remove programs appwiz.cpl Administrative Tools control admintools Computer Management compmtmt.msc Date & Time timedate.cpl Device Manager devmgmt.msc Display properties desk.cpl Event Viewer eventvwr.msc Internet Properties inetcpl.cpl Local Users and Groups lusrmgr.msc Mouse properties main.cpl Network Connections ncpa.cpl Power configuration powercfg.cpl Printers And Faxes control printers Registry editor regedit Scheduled Tasks control schedtasks Services services.msc Sound and Audio settings mmsys.cpl System Properties sysdm.cpl Windows Task Manager taskmgr Windows Firewall Settings firewall.cpl
Some commands useful in XP professional or windows domain env. are as below
| TASK | Command |
| Group Policy Editor | gpedit.msc |
| Computer Managment | compmgmt.msc |
| Security Center | wscui.cpl |
| Group policy update | gpupdate |
| Disk Management | diskmgmt.msc |
But before you launch any applications, you should make a registry edit, to change the value of HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Separate Process value to “1”. To do so, launch the command prompt as the administrator using the command below:
Now in the command prompt, type in regedit. This will openup registry editor for you. Navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced, and change the registry key “SeparateProcess” value to “1” as shown below":
Without the registry entry, more than half the commands listed will fail, or will produce no output.
You can right-click on any executable and select “Run as” option as shown below, to launch an installation or any executable:
You will not be able to do the same with MSI install packages. You will have to launch a command prompt as administrator, navigate to the location of the MSI installer package and execute it from there.
And, yes your observation is correct. I customized my administrator command window to look different. It is fairly easy to do so with cmd.exe extensions. I have a shortcut made on my desktop to launch the command prompt as administrator. The shortcut is as below:
%windir%\system32\runas.exe /user:administrator "cmd.exe /k cd c:\ && color f5 && title *****Local Admin console *****"
I also have a shortcut key assigned, enabling me to launch the administrator command window, from my keyboard. In my case, I have it as Ctrl + Alt + L.
There are couple of limitations as to what you can and what you cannot do with this administrator command prompt window. One major drawback is that you cannot launch Windows Update from this window. But this draw back is easily overcome by adjusting your windows update parameters in control panel to update automatically.
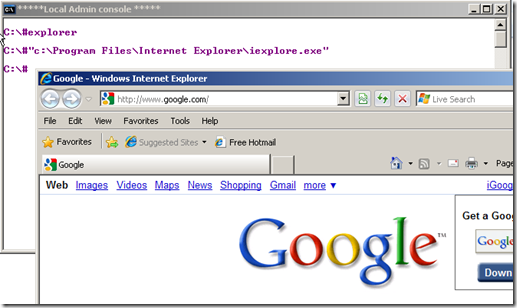
You can Launch Windows Explorer as administrator by typing in “Explorer” in the command window
You can launch IE as an administrator (useful, when you have to update adobe flash plugin etc.,) by typing the complete path to IE as shown below:
There are a lot of tasks you can perform using the windows command prompt launched as the administrator. Running as a limited user will help you stay safe, and the “Run as” options listed above will ensure that you do not miss the functionality either.